Foam Fabrication
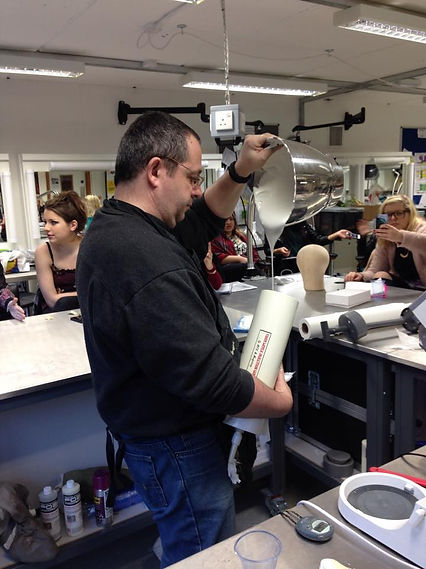






Injecting
-
High solid latex foaam base-creamed latex, different from liquid latex. White in colour. The main component of foam latex
-
Foaming agent-Thick liquid, mainly composed of castor oil (soap) and water. This will help your foam reach the volume you want when whisked. 20% of this to the latex base
-
curing agent- grey liquid, helps set the batch of foam. It goes from a shaving foam state to a compact solid. The amount depends on different factors: temperature, humidity, the refining time. Usually between 10-14% of the amount of latex base but could be less if the room temperature is higher than 20c.
-
release agent-pearly foam brushed in plaster moulds. Temporarely seaals the porus surface of the mould. Can be used on fibreglass moulds when damaged, to avoid the foam grabbing onto cracks. No need to use this on details.
Components
-
Always wear gloves
-
do not drink eat or smoke when you run foam
-
wear appropriate clothing
-
work in a well ventilated area
-
avoid contact with skin and eyes. If projection in eye was with running water
-
it is best to dispose of foam when it is set rather than in liquid form. Do not throw in sink
Health and Safety
An example of a foam latex arm from the film Wolf Man
Shelve life-
-
The ammonia will go off first, it will evaporate. Shelf life for latex is 6months a year maximum
-
in order to keep the foam latex kit usuable for as long as possible shake for a few minutes each on each container, every couple of weeks, to avoid the different products to seperate and settle at the bottom
-
has to be kept away from sunlight and freezing temperature
-
keep them in a dry place, off the ground if possible
-
try to avoid ordering kits in the winter when the temperature is very low
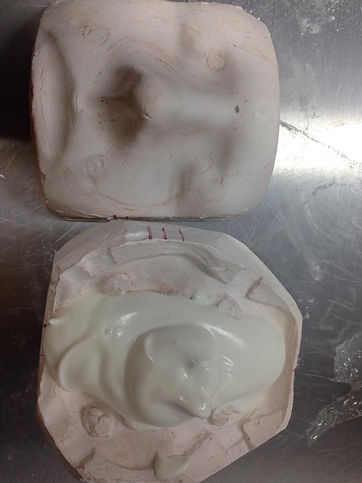
Different types & materials of moulds you can run your foam in -
-
plaster-before to remove the mould it needs to cool down
-
synthetic plaster moulds- heavy, sturdier as the water is replaced with resin
-
fibreglass-no porous, but you need bleeder holes for the steam to escape
-
epoxy resin moulds, need to be baked for one day at an increasing temperature
-
polyurethane resin moulds (light and strong, different powders can be added to the 2 parts mix to make them lighter, stronger, withstand heat better
-
silicone mould/jacket moulds (silicone-non-porous material, and you can't drill bleeder holes in it. In order to reduce steam collapse as much as possible- the foam being pulled away from the silicone while baking out- you can spray permanent spray glue on to the silicone
Bleeder holes
-
bleeder holes allow 3things when it comes to injecting foam latex into fibreglass or polyurethane mould: you can visually control how your mould is filled, it pushes out any air trapped, it levels the pressure up inside the mould, reducing shrinkage of the foam piece
Different ways of filling up your moulds (with a brush or by injection)
Manually- mould lays open, foam brush in. This works for small moulds, or when you don't have time to install an injecton. Brush a thin layer of foam first, to capture all the details, then, without trapping any air pockets, add more foam on top. This is how the mould below has been filled.
By injection-
With an injection syringe, you inject foam in a closed mould, until the foam comes out by the bleeder holes, through the flashing.
First run of foam-
-
keep a note of everything during the process, and make sure you have everything you need, so if you have to do it again you can adjust the original. You need to write down:
-
the date
-
brand/number of the mixer
-
room temp
-
humidity level
-
quantity of base latex you use in the mix
-
quantity of foaming agent (20% of the amount of latex base used)
-
quantity of curing agent (10% of the amount of latex base used)
-
quantity of gelling agent (depending on the room temperature, humidity etc, is between 5-15% of the amount of latex
-
quantity of stabilizer agent used
-
quantity of potassium oleate
-
time needed for the foam ro rise the volume/aspect desired
-
time needed to refine your mix
-
final aspect of the foam
-
final result
-
The size of your mix depends on how many moulds you will have to fill up. To measure, keep the material you sculpted with, place in your mixer to visualise the volume
-
weigh latex base, foaming agent (20%), curing agent (10%), add the colours or any additive you need.
-
Start whisking at high speed, start the stop watch
-
weigh the gelling agent and place aside
-
it could take 3-6 minutes for the foam to rise
-
turn the mixer down to slow the setting
-
refining the foam means breaking the big air bubbles, this could take 10 to 20 minutes to get a smooth aspect
-
now you can use mould release on your moulds.
-
once it looks like shaving foam you are ready to add the gelling agent
-
leave the mixer go for an extra 1 minute 30 seconds at the same speed
-
now you have 10-30 minutes to either brush the foam in, or fill up the syringe
-
once the foam is thoroughly gelled (30 min) it is time to bake ( it takes 1hour of baking time per centimetrer of thickness of the mould
-
when it is ready the foam should spring back.
Two ways of pre painting: Dick smith amadayas makeup. Glue on with prosade. Transfer onto the skin, dry with a hair dryer. Work from the inside to the outside. Foam is porous so it will dry when the piece is down. With foam it is less important that the prosade is clear because it is porous it will dry. Glue the edges. Try not to powder too much. Use Cabo patch. Cabosil and prosade glue. To fill the edges because we can't dissolve the edges with film. Fm Abraham. Amadayas makeup you can see the powder from layering the Cabo patch. It might shrink when you dry it so you may need to apply again. The filler creates a smooth shiny edge around the prosthetic which isn't natural so you can stipple prosade on top to get a more realistic texture. Keep working until there is a subtle edge blended into the skin. Grease paints will attack the foam. Illustrator will just be soaked up so it needs to be sealed. Stipple over prosade to create a sealer. Powder wIth translucent powder. Rubber mask greasepaint for foam latex but it is very exspensive. Alcohol with grease. But if you leave it it will curdle. Common to start off with a red blood layer and then build up flesh layers.
Foam Latex Application